Set of demos to demonstrate Envoy Proxy features
HTTP Routing: Simple Match Routing
All traffic is routed by the front envoy to the service containers. Internally the traffic is routed to the service envoys, then the service envoys route the request to the flask app via the loopback address. In this demo, all traffic is routed to the service envoys like this:
- A request (path
/service/blue& port8000) is routed toservice_blue - A request (path
/service/green& port8000) is routed toservice_green - A request (path
/service/red& port8000) is routed toservice_red
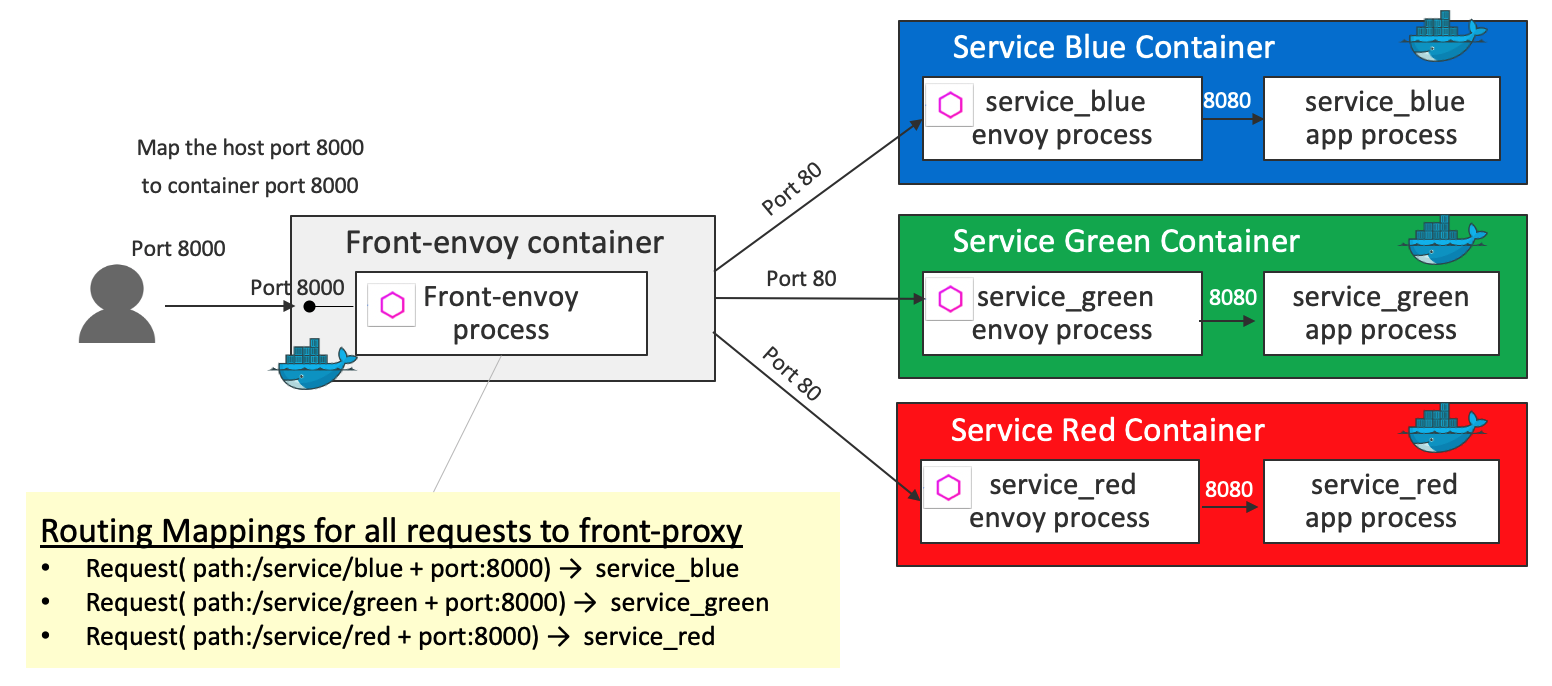
Key definition 1 - virtual_hosts in front-envoy.yaml
virtual_hosts:
- name: backend
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
route:
cluster: service_green
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
route:
cluster: service_blue
- match:
prefix: "/service/red"
route:
cluster: service_red
Key definition 2 - clusters in front-envoy.yaml
clusters:
- name: service_blue
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_blue
port_value: 80
- name: service_green
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_green
port_value: 80
- name: service_red
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_red
port_value: 80
To continue, go to github
HTTP Routing: Routing based on Header Condition
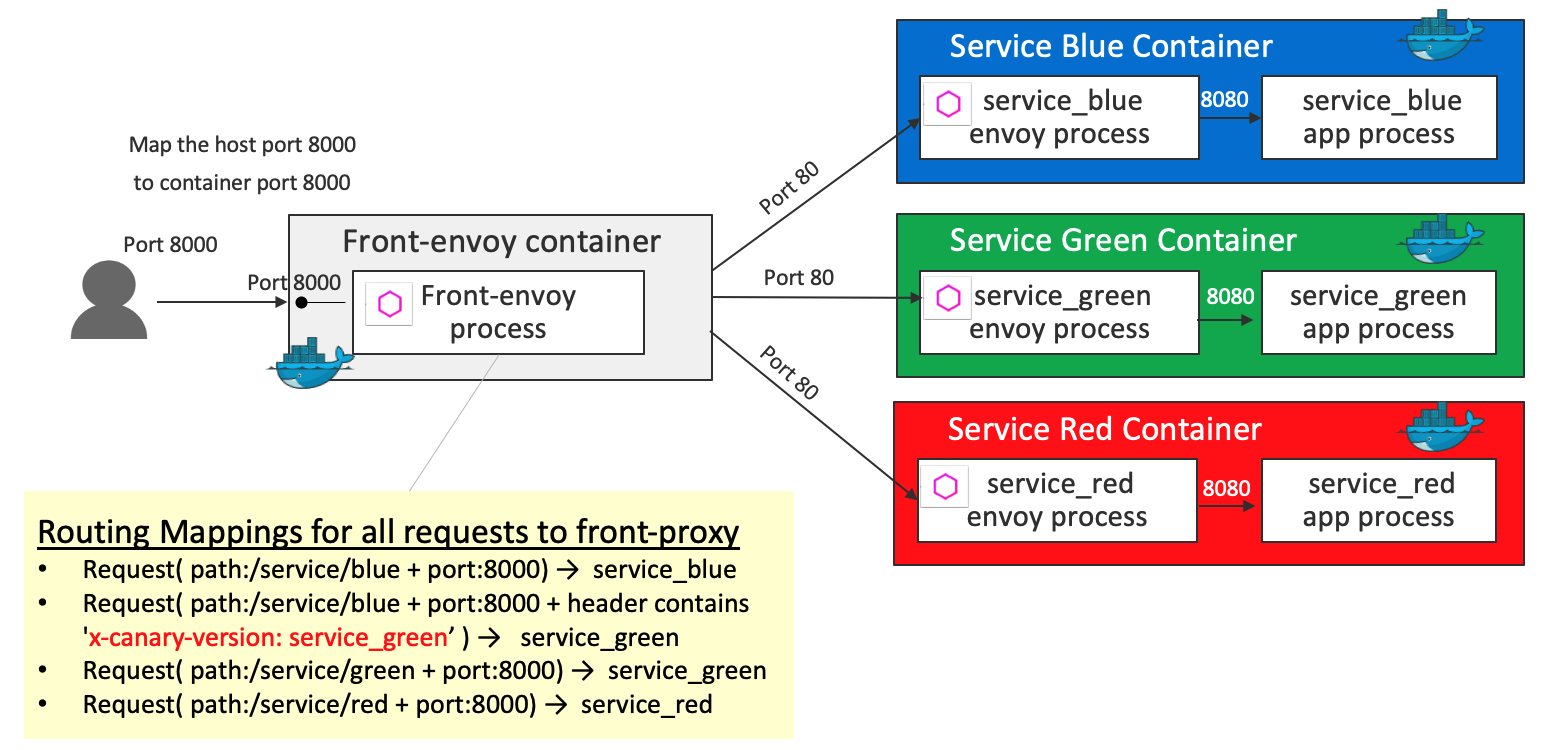
Key definition 1 - virtual_hosts in front-envoy.yaml
virtual_hosts:
- name: backend
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
headers:
- name: "x-canary-version"
exact_match: "service_green"
route:
cluster: service_green
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
route:
cluster: service_blue
- match:
prefix: "/service/red"
route:
cluster: service_red
Key definition 2 - clusters in front-envoy.yaml
clusters:
- name: service_blue
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_blue
port_value: 80
- name: service_green
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_green
port_value: 80
- name: service_red
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_red
port_value: 80
To continue, go to github
HTTP Routing: Blue Green Traffic Splitting
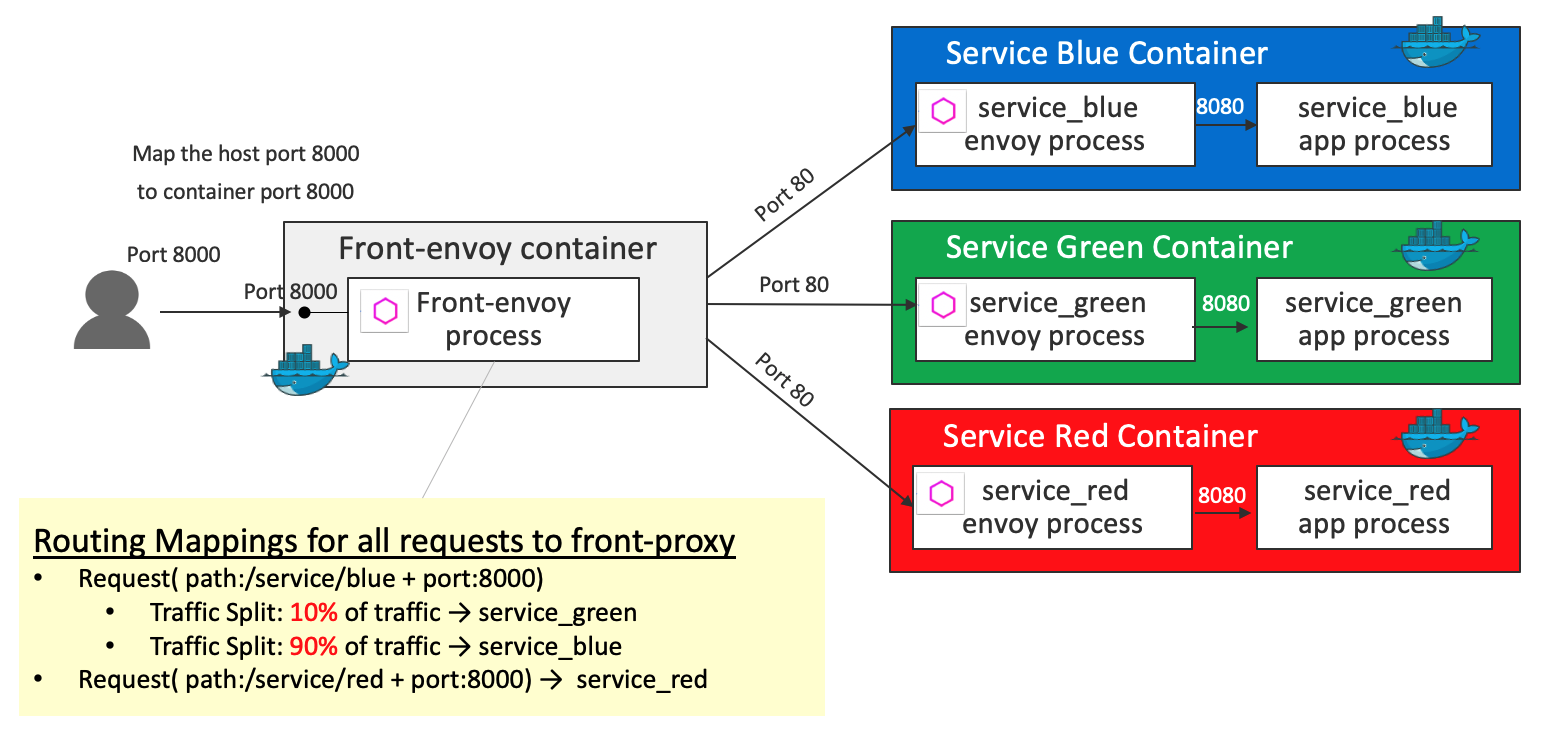
Key definition 1 - virtual_hosts in front-envoy.yaml
virtual_hosts:
- name: backend
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
route:
weighted_clusters:
clusters:
- name: service_green
weight: 10
- name: service_blue
weight: 90
- match:
prefix: "/service/red"
route:
cluster: service_red
Key definition 2 - clusters in front-envoy.yaml
clusters:
- name: service_blue
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_blue
port_value: 80
- name: service_green
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_green
port_value: 80
- name: service_red
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
http2_protocol_options: {}
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: service_red
port_value: 80
To continue, go to github
Fault Injection
Fault injection is a technique for improving the coverage of a test by introducing faults to test code paths, in particular error handling code paths, that might otherwise rarely be followed. The filter ( http_filters in the demo ) can be used to inject delays and abort requests with user-specified error codes.
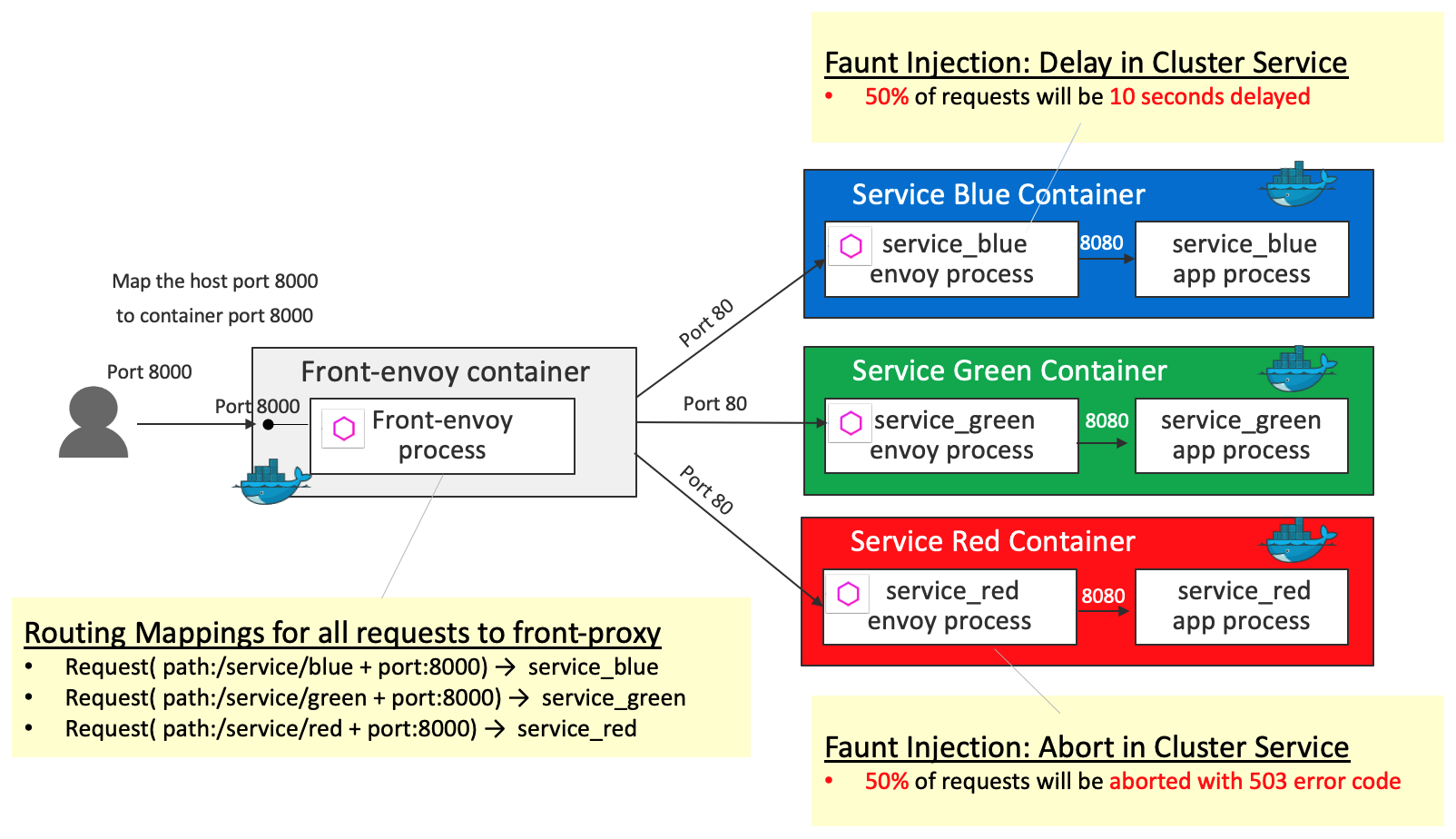
Front-proxy configurations are the same as the ones in HTTP Routing: Simple Match Routing. Differences from HTTP Routing: Simple Match Routing are the following 2 fault injections:
- Fault injection
abort(50% of requests will be aborted with 503 error code) for the requests toservice_red - Fault injection
delay(50% of requests will be 10 seconds delayed) for the requests toservice_blue
Key definition 1 - http_filters in service-envoy-fault-injection-abort.yaml
http_filters:
- name: envoy.fault
config:
abort:
http_status: 503
percentage:
numerator: 50
denominator: HUNDRED
For
numeratoranddenominatorofpercentage, see type.FractionalPercent
Key definition 2 - http_filters in service-envoy-fault-injection-delay.yaml
http_filters:
- name: envoy.fault
config:
delay:
type: fixed
fixed_delay: 10s
percentage:
numerator: 50
denominator: HUNDRED
For
fixed_delayandpercentageof delay injection, see config.filter.fault.v2.FaultDelay
To continue, go to github
Circuit Breaker
Circuit Breaking lets you configure failure thresholds that ensure safe maximums after which these requests stop. This allows for a more graceful failure, and time to respond to potential issues before they become larger.
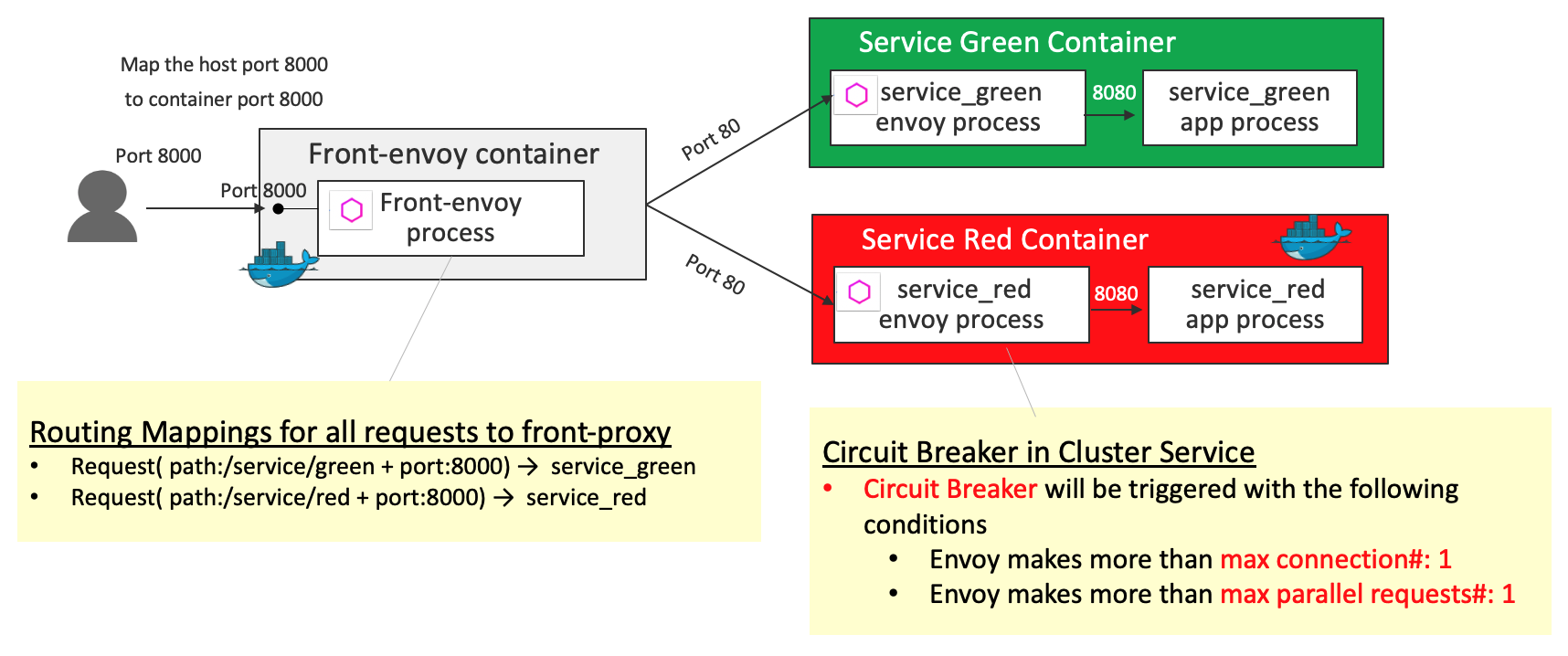
- Circuit Breaker is configured in
service_redsuch that Circuit Breaker will be triggered with the following conditions:- Envoy makes more than
max connection#:1 - Envoy makes more than
max parallel requests#:1
- Envoy makes more than
Key definition - clusters in service-envoy-circuitbreaker.yaml
clusters:
- name: local_service
connect_timeout: 0.25s
type: strict_dns
lb_policy: round_robin
circuit_breakers:
thresholds:
max_connections: 1
max_pending_requests: 1
max_requests: 1
hosts:
- socket_address:
address: 127.0.0.1
port_value: 8080
For the detail of
circuit_breakersconfiguration, see cluster.CircuitBreakers
To continue, go to github
Timeouts and Retries
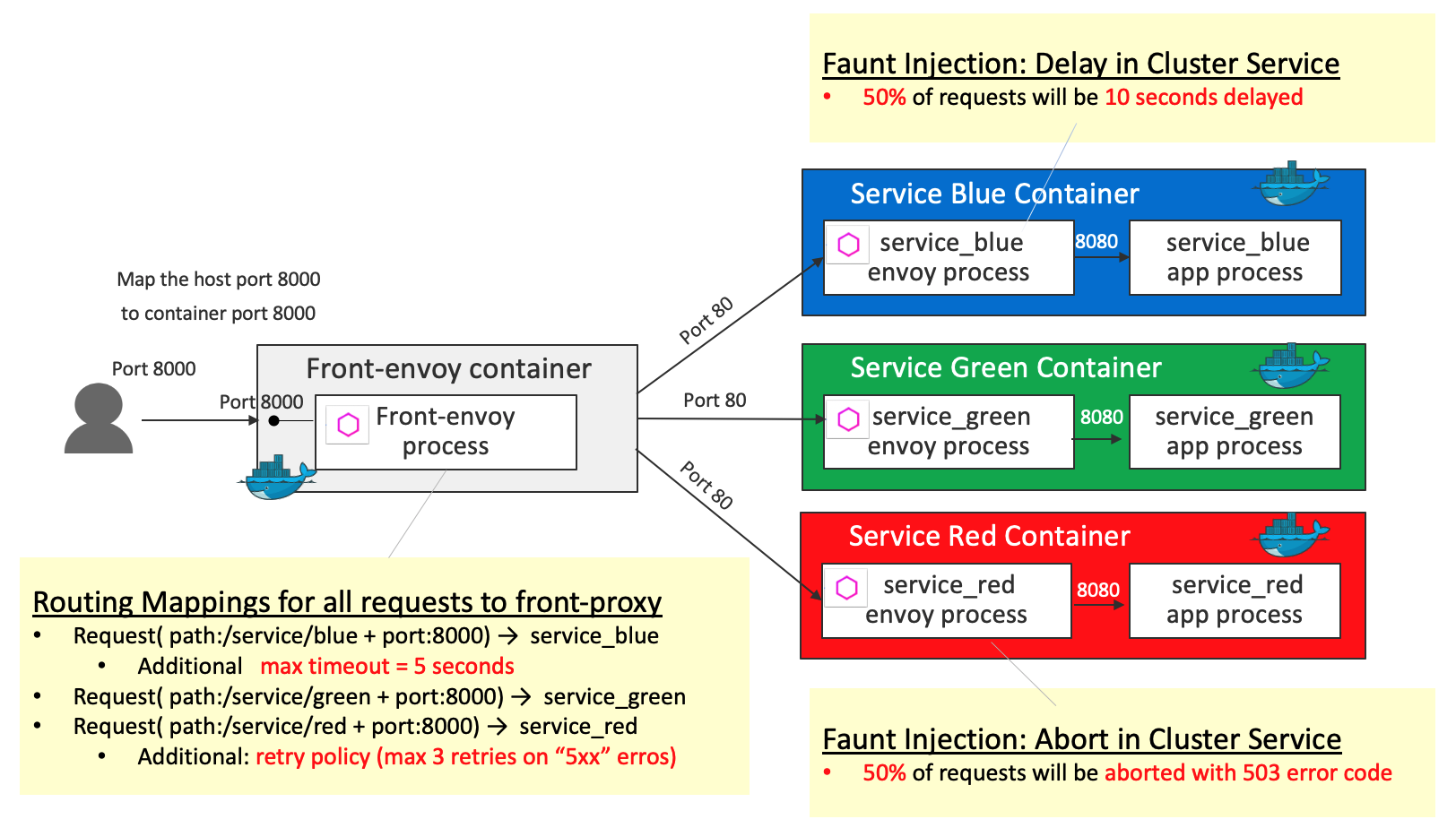
Front-proxy configurations are the same as the ones in HTTP Routing: Simple Match Routing. Differences from HTTP Routing: Simple Match Routing are the following 2 additional behaviors:
Timeouts(5 seconds) for the request toservice_blueRetriesthat Envoy will attempt to do ifservice_redresponds with any 5xx response code
For Service Containers, delay fault injection and abort fault injection are configured in service_blue and service_red respectively (which are the same configuration as the ones in Fault Injection Demo)
Key definition - virtual_hosts in front-envoy.yaml
virtual_hosts:
- name: backend
domains:
- "*"
routes:
- match:
prefix: "/service/blue"
route:
cluster: service_blue
timeout: 5s
- match:
prefix: "/service/green"
route:
cluster: service_green
- match:
prefix: "/service/red"
route:
cluster: service_red
retry_policy:
retry_on: "5xx"
num_retries: 3
per_try_timeout: 5s
timeout: (Duration) Specifies the timeout for the route. If not specified, the default is 15s. For more detail, seetimeoutsection in RouteActionretry_policyindicates the retry policy for all routes in this virtual host. For more detail on retry_policy, see route.RetryPolicy
To continue, go to github